whatsapp:+86 13622680352

How to Select the Right Rated Torque and Accuracy of RV Reducer for Robotic Arm
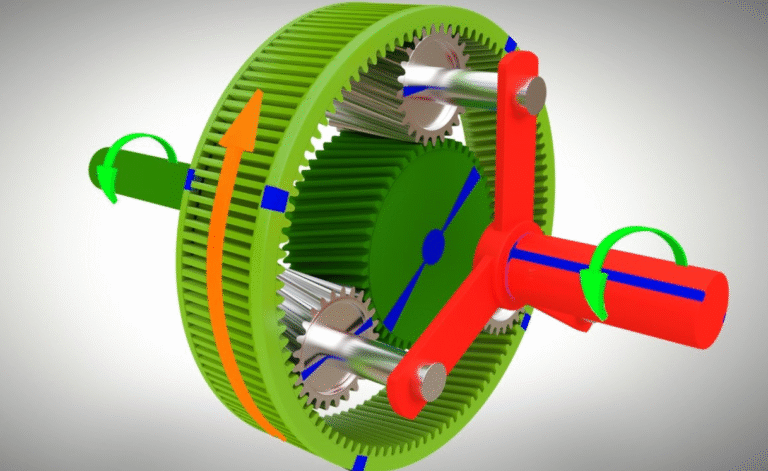
Choosing the correct RV reducer for a robotic arm is one of the most critical engineering decisions in modern automation. The reducer directly influences the robot’s load capacity, trajectory accuracy, long-term stability, and overall lifespan. While there are many reducer types available—planetary gearboxes, harmonic drives, cycloidal reducers—the RV reducer remains the preferred solution for medium and heavy-duty robotic joints due to its high rigidity, extremely low backlash, and superior shock-load tolerance.
This article explains how to scientifically select the rated torque and precision grade of an RV reducer according to the robot’s load, dynamic performance, and accuracy targets. It provides engineering methods, formulas, and practical considerations based on industrial practice. As a professional transmission manufacturer, NUODUN supports OEM and customized gearbox design for robot and automation integrators.

Why RV Reducers Matter in Robotic Arms
In an articulated robotic arm, each joint must provide both strength and precision. Unlike typical machinery, a robot’s joints experience:
- Varying loads across the working envelope
- Frequent direction changes
- High dynamic responses
- Continuous micro-positioning
- Long operational cycles
RV reducers are commonly used in the base, shoulder, and elbow joints because these axes carry the highest loads and determine the overall stiffness of the robot. Selecting the correct reducer prevents:
- Excess vibration
- Positioning drift
- Excessive heating
- Poor repeatability
- Early mechanical failures
Proper selection is essential for stable robotic performance.

Determining the Rated Torque Requirement
Selecting the correct torque rating is the foundation of RV reducer sizing.
1. Calculate the Maximum Load Torque
Every robotic joint experiences a maximum load under the most demanding operating condition. This is usually:
- Maximum payload the robot carries
- Arm length contributing to leverage
- Gravity or task-induced forces
- Dynamic forces from acceleration and deceleration
A common engineering formula for calculating required output torque is: T=F×L×KsT = F \times L \times K_sT=F×L×Ks
Where:
T = required output torque
F = applied force or payload equivalent force
L = working arm length
K_s = safety factor (commonly 1.3 to 2.0 depending on conditions)
In robotics, the torque should never be selected based solely on static load. Robots move constantly, and acceleration forces can easily exceed static values.
2. Apply a Safe Torque Utilization Ratio
RV reducer specifications list rated torque, which should be used in combination with the real load.
A safe working guideline is:
Actual working torque / Rated torque ≤ 0.6–0.8
- ≤0.6 for high-speed, high-cycle robots
- ≤0.7–0.8 for moderate loads
- ≤0.5 for precision or high-temperature environments
A reducer that is too small will overheat, experience excessive wear, and lose accuracy prematurely.
3. Consider Shock and Dynamic Loads
Robots often undergo:
- Frequent start/stop actions
- Sudden direction reversals
- Emergency braking
- High-acceleration movements
These conditions generate impact torque that can be 2.5× to 5× the rated torque.
High-quality RV reducers are designed to withstand short-term shock loads significantly above rated torque. Always check:
- Allowable starting/stopping torque
- Maximum instantaneous overload capacity
If your robot performs welding, machining, rapid pick-and-place, or tasks with vibration, shock resistance becomes a key parameter.
Selecting the Required Precision Level (Backlash and Rigidity)
Accuracy is just as important as torque. The reducer’s internal mechanical characteristics directly determine the robot’s positioning quality.
1. Understanding Backlash and Its Impact
Backlash is the small angular play that appears during direction changes. In precision robotic joints, excessive backlash results in:
- Poor trajectory tracking
- End-effector micro-shaking
- Reduced repeatability
- Inconsistent machining/welding lines
- Difficulty achieving accurate assembly tasks
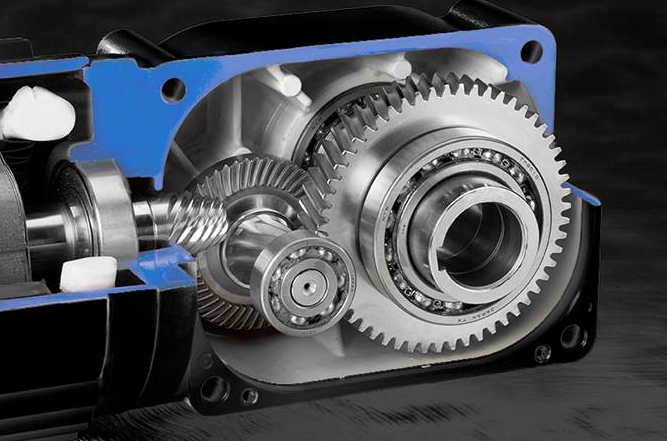
RV reducers are known for extremely low backlash due to their multi-tooth engagement and rigid cycloidal structure.
2. Required Backlash Values for Robots
Different robotic applications have different accuracy needs:
| Application Type | Recommended Backlash |
|---|---|
| Industrial robots (general) | ≤1–2 arcmin |
| High-precision robots | ≤1 arcmin |
| Semiconductor, optical, medical equipment | ≤0.5 arcmin |
| Ultra-precision robotic systems | ≤0.3 arcmin |
Most industrial robotic arms adopt RV reducers with 1 arcmin or lower backlash at major axes.
3. Consider Rigidity, Not Just Backlash
Precision is not determined by backlash alone. Rigidity is equally important.
A reducer with insufficient torsional stiffness will cause:
- Micro-vibrations
- Overshoot during acceleration
- Difficulty maintaining stable high-speed paths
- Lower machining quality
Load-bearing joints such as the base and shoulder often require the highest rigidity.
4. Influence of Servo Motor + RV Reducer Combination
The total positioning accuracy of the robot comes from:
Servo motor accuracy + RV reducer accuracy + mechanical structural rigidity
Even a high-precision reducer cannot compensate for:
- Poor servo tuning
- Heavy end loads
- Low-rigidity link structure
Therefore, reducer selection must be combined with full system analysis.
Practical Engineering Recommendations for Proper RV Reducer Selection
1. Review Rated Life and Duty Cycle
Robots operate with:
- Long daily runtimes
- Repetitive cycling
- High shock loads
Select a reducer that meets:
- Required operating lifespan
- Duty cycle performance
- Heat dissipation capability
2. Evaluate Dynamic Loads Through Simulation
For high-speed or multi-axis robots:
- Use CAD+CAE simulation
- Estimate inertia loads
- Analyze torque peaks along trajectories
Simulation avoids under-sizing and improves long-term reliability.
3. Select Lubrication That Matches Application Conditions
Temperature, load, and speed affect:
- Oil viscosity
- Lubrication intervals
- Heat generation
Follow the manufacturer’s lubrication guidelines for optimal performance.
4. Work Directly with the Manufacturer for Complex Applications
For custom or high-precision robotics, collaborate with engineering teams to determine:
- Correct reduction ratio
- Housing and flange configuration
- Backlash classification
- Shaft alignment
- Special mounting requirements
- Extreme-environment modifications
NUODUN provides OEM customization services for unique robotic applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How much torque margin should I use when sizing an RV reducer?
A utilization ratio of 0.6–0.8 is standard. Use ≤0.6 for high-cycle tasks or precision robots.
2. What backlash value is appropriate for industrial robotic arms?
Most robots require ≤1 arcmin, while high-precision equipment targets ≤0.5 arcmin or lower.
3. Can an RV reducer handle frequent start-stop operations?
Yes. RV reducers are designed for impact environments and can tolerate 2.5× to 5× rated torque during short-term shock.
4. Does reduction ratio affect robot precision?
Yes. Higher ratios reduce servo motor influence and increase stability but may reduce speed. Proper selection depends on the joint’s function.
5. Does NUODUN offer OEM and customized RV reducers?
Yes. NUODUN provides OEM/ODM support including custom ratios, flanges, lubrication schemes, and precision classifications.
Conclusion: Achieving Optimal Robot Performance with Proper RV Reducer Selection
Selecting the correct rated torque and accuracy for an RV reducer is essential for ensuring that a robotic arm performs with stability, safety, and repeatability over its entire lifespan. Proper torque margins prevent overload failures, while precision-rated reducers maintain accurate trajectories and high-quality end-effector control.
With decades of manufacturing expertise in precision transmission systems, NUODUN provides high-rigidity, low-backlash RV reducers designed specifically for robotic applications. Whether for industrial automation, collaborative robots, or high-precision machinery, NUODUN offers expert engineering support and OEM customization to meet complex requirements.
Need help selecting the right RV reducer for your robotic arm?
Contact NUODUN’s engineering team today for professional sizing support and OEM customization options.